Portal:Stars
IntroductionA star is a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated 1022 to 1024 stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye—all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material largely comprising hydrogen, helium, and trace heavier elements. Its total mass mainly determines its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due to the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core. This process releases energy that traverses the star's interior and radiates into outer space. At the end of a star's lifetime as a fusor, its core becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or—if it is sufficiently massive—a black hole. Stellar nucleosynthesis in stars or their remnants creates almost all naturally occurring chemical elements heavier than lithium. Stellar mass loss or supernova explosions return chemically enriched material to the interstellar medium. These elements are then recycled into new stars. Astronomers can determine stellar properties—including mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), variability, distance, and motion through space—by carrying out observations of a star's apparent brightness, spectrum, and changes in its position in the sky over time. Stars can form orbital systems with other astronomical objects, as in planetary systems and star systems with two or more stars. When two such stars orbit closely, their gravitational interaction can significantly impact their evolution. Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a star cluster or a galaxy. (Full article...) Selected star -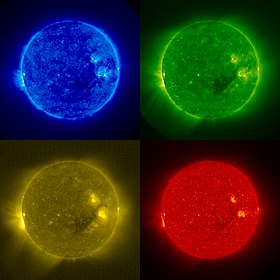 Photo credit: NASA's STEREO
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. The Sun has a diameter of about 1,392,000 kilometers (865,000 mi) (about 109 Earths), and by itself accounts for about 99.86% of the Solar System's mass; the remainder consists of the planets (including Earth), asteroids, meteoroids, comets, and dust in orbit. About three-quarters of the Sun's mass consists of hydrogen, while most of the rest is helium. Less than 2% consists of other elements, including iron, oxygen, carbon, neon, and others. The Sun's color is white, although from the surface of the Earth it may appear yellow because of atmospheric scattering. Its stellar classification, based on spectral class, is G2V, and is informally designated a yellow star, because the majority of its radiation is in the yellow-green portion of the visible spectrum. In this spectral class label, G2 indicates its surface temperature of approximately 5,778 K (5,505 °C), and V (Roman five) indicates that the Sun, like most stars, is a main sequence star, and thus generates its energy by nuclear fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium. Selected article -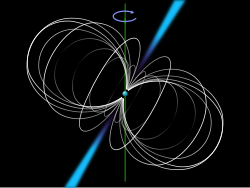 Photo credit: User:Mysid and User:Jm smits
Pulsars are highly magnetized, rotating neutron stars that emit a beam of electromagnetic radiation. The observed periods of their pulses range from 1.4 milliseconds to 8.5 seconds. The radiation can only be observed when the beam of emission is pointing towards the Earth. This is called the lighthouse effect and gives rise to the pulsed nature that gives pulsars their name. Because neutron stars are very dense objects, the rotation period and thus the interval between observed pulses is very regular. For some pulsars, the regularity of pulsation is as precise as an atomic clock. A few pulsars are known to have planets orbiting them, such as PSR B1257+12. Werner Becker of the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics said in 2006, "The theory of how pulsars emit their radiation is still in its infancy, even after nearly forty years of work. The events leading to the formation of a pulsar begin when the core of a massive star is compressed during a supernova, which collapses into a neutron star. The neutron star retains most of its angular momentum, and since it has only a tiny fraction of its progenitor's radius (and therefore its moment of inertia is sharply reduced), it is formed with very high rotation speed. A beam of radiation is emitted along the magnetic axis of the pulsar, which spins along with the rotation of the neutron star. The magnetic axis of the pulsar determines the direction of the electromagnetic beam, with the magnetic axis not necessarily being the same as its rotational axis. This misalignment causes the beam to be seen once for every rotation of the neutron star, which leads to the "pulsed" nature of its appearance. The beam originates from the rotational energy of the neutron star, which generates an electrical field from the movement of the very strong magnetic field, resulting in the acceleration of protons and electrons on the star surface and the creation of an electromagnetic beam emanating from the poles of the magnetic field. This rotation slows down over time as electromagnetic power is emitted. When a pulsar's spin period slows down sufficiently, the radio pulsar mechanism is believed to turn off (the so-called "death line"). As this seems to take place after ~10-100 million years, but neutron stars have been formed throughout the ~13.6 billion year age of the universe, more than 99% of neutron stars are thought to no longer be pulsars. To date, the slowest observed pulsar has a period of 8 seconds. Selected image - Photo credit: NASA
The Crab Nebula (catalogue designations M1, NGC 1952, Taurus A) is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus. The nebula was observed by John Bevis in 1731; it corresponds to a bright supernova recorded by Chinese and Arab astronomers in 1054. At X-ray and gamma-ray energies above 30 KeV, the Crab is generally the strongest persistent source in the sky, with measured flux extending to above 1012 eV. Located at a distance of about 6,500 light-years (2 kpc) from Earth, the nebula has a diameter of 11 ly (3.4 pc) and expands at a rate of about 1,500 kilometers per second. At the center of the nebula lies the Crab Pulsar, a rotating neutron star, which emits pulses of radiation from gamma rays to radio waves with a spin rate of 30.2 times per second. The nebula acts as a source of radiation for studying celestial bodies that occult it. Did you know?
SubcategoriesTo display all subcategories click on the ►
Selected biography - Photo credit: Portrait from Toruń
Nicolaus Copernicus (19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was the first astronomer to formulate a comprehensive heliocentric cosmology, which displaced the Earth from the center of the universe. Nicolaus Copernicus was born on 19 February 1473 in the city of Toruń (Thorn) in Royal Prussia, part of the Kingdom of Poland. Copernicus' epochal book, De revolutionibus orbium coelestium (On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres), published just before his death in 1543, is often regarded as the starting point of modern astronomy and the defining epiphany that began the scientific revolution. His heliocentric model, with the Sun at the center of the universe, demonstrated that the observed motions of celestial objects can be explained without putting Earth at rest in the center of the universe. His work stimulated further scientific investigations, becoming a landmark in the history of science that is often referred to as the Copernican Revolution. Among the great polymaths of the Renaissance, Copernicus was a mathematician, astronomer, physician, quadrilingual polyglot, classical scholar, translator, artist, Catholic cleric, jurist, governor, military leader, diplomat and economist. Among his many responsibilities, astronomy figured as little more than an avocation – yet it was in that field that he made his mark upon the world.
TopicsThings to do
Related portalsAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals |