Portal:Viruses
The Viruses Portal
Welcome!
Viruses are small infectious agents that can replicate only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all forms of life, including animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and archaea. They are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most abundant type of biological entity, with millions of different types, although only about 6,000 viruses have been described in detail. Some viruses cause disease in humans, and others are responsible for economically important diseases of livestock and crops.
Virus particles (known as virions) consist of genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA, wrapped in a protein coat called the capsid; some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope. The capsid can take simple helical or icosahedral forms, or more complex structures. The average virus is about 1/100 the size of the average bacterium, and most are too small to be seen directly with an optical microscope.
The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids, others from bacteria. Viruses are sometimes considered to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce and evolve through natural selection. However they lack key characteristics (such as cell structure) that are generally considered necessary to count as life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as "organisms at the edge of life".
Selected disease
Cervical cancer is a tumour of the cervix, the part of the uterus that adjoins the vagina in the female reproductive tract. Certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) are implicated in more than 90% of these cancers, although the great majority of HPV infections of the cervix are not associated with cancer. HPV is transmitted by vaginal sex, infecting cervical epithelial cells. In a minority of cases, infection persists for years, and pre-cancerous changes called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia can develop, which sometimes progress to cancer. Squamous cell carcinomas are the most common. HPV infection is considered essential for nearly all forms of cervical cancer to develop, but other risk factors are also involved, including smoking, HIV infection and other forms of immune suppression, and long-term use of oral contraceptives.
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women worldwide. It can be detected by screening; screening every 3–5 years, with appropriate follow-up, can reduce cancer incidence by up to 80%. HPV vaccines protect against high-risk virus strains, and can prevent up to 90% of cervical cancers. Where screening and vaccination are not available, cervical cancer has substantial mortality; worldwide, an estimated 569,000 cases and 311,000 deaths occurred in 2018, with around 85% of cases being in developing countries.
Selected image
HIV-1 budding from lymphocytes in culture. HIV establishes a latent infection in several types of immune cell and causes profound immunodeficiency.
Credit: C. Goldsmith (1984)
In the news
26 February: In the ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), more than 110 million confirmed cases, including 2.5 million deaths, have been documented globally since the outbreak began in December 2019. WHO
18 February: Seven asymptomatic cases of avian influenza A subtype H5N8, the first documented H5N8 cases in humans, are reported in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia, after more than 100,0000 hens died on a poultry farm in December. WHO
14 February: Seven cases of Ebola virus disease are reported in Gouécké, south-east Guinea. WHO
7 February: A case of Ebola virus disease is detected in North Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. WHO
4 February: An outbreak of Rift Valley fever is ongoing in Kenya, with 32 human cases, including 11 deaths, since the outbreak started in November. WHO
21 November: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gives emergency-use authorisation to casirivimab/imdevimab, a combination monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy for non-hospitalised people twelve years and over with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, after granting emergency-use authorisation to the single mAb bamlanivimab earlier in the month. FDA 1, 2
18 November: The outbreak of Ebola virus disease in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, which started in June, has been declared over; a total of 130 cases were recorded, with 55 deaths. UN
Selected article
Vaccination or immunisation is the administration of immunogenic material (a vaccine) to stimulate an individual's immune system to develop adaptive immunity to a virus or other pathogen, and so develop protection against an infectious disease. The active agent of a vaccine may be intact but inactivated or weakened forms of the pathogen, or purified highly immunogenic components, such as viral envelope proteins. Smallpox was the first disease for which a vaccine was produced, by Edward Jenner in 1796.
Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing infectious diseases and can also ameliorate the symptoms of infection. When a sufficiently high proportion of a population has been vaccinated, herd immunity results. Widespread immunity due to mass vaccination is largely responsible for the worldwide eradication of smallpox and the elimination of diseases such as polio from much of the world. Since their inception, vaccination efforts have met with objections on scientific, ethical, political, medical safety and religious grounds, and the World Health Organization considers vaccine hesitancy an important threat to global health.
Selected outbreak
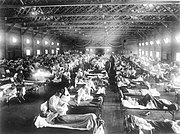
The 1918–20 influenza pandemic, the first of the two involving H1N1 influenza virus, was unusually deadly. It infected 500 million people across the entire globe, with a death toll of 50–100 million (3–5% of the world's population), making it one of the deadliest natural disasters of human history. It has also been implicated in the outbreak of encephalitis lethargica in the 1920s. Despite the nickname "Spanish flu", the pandemic's geographic origin is unknown.
Most influenza outbreaks disproportionately kill young, elderly or already weakened patients; in contrast this predominantly killed healthy young adults. Contemporary medical reports suggest that malnourishment, overcrowded medical facilities and poor hygiene promoted fatal bacterial pneumonia. Some research suggests that the virus might have killed through a cytokine storm, an overreaction of the body's immune system. This would mean the strong immune reactions of young adults resulted in a more severe disease than the weaker immune systems of children and older adults.
Selected quotation
| “ | Viruses are living chemicals... | ” |
Recommended articles
Viruses & Subviral agents: bat virome • elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus • HIV • introduction to viruses![]() • Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus
• Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus![]() • virus
• virus![]()
Diseases: colony collapse disorder • common cold • croup • dengue fever![]() • gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza
• gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza![]() • meningitis
• meningitis![]() • myxomatosis • polio
• myxomatosis • polio![]() • pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
• pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
Epidemiology & Interventions: 2007 Bernard Matthews H5N1 outbreak • Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations • Disease X • 2009 flu pandemic • HIV/AIDS in Malawi • polio vaccine • Spanish flu • West African Ebola virus epidemic
Virus–Host interactions: antibody • host • immune system![]() • parasitism • RNA interference
• parasitism • RNA interference![]()
Methodology: metagenomics
Social & Media: And the Band Played On • Contagion • "Flu Season" • Frank's Cock![]() • Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa
• Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa![]() • social history of viruses
• social history of viruses![]() • "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
• "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
People: Brownie Mary • Macfarlane Burnet![]() • Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C
• Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C![]() • HIV-positive people
• HIV-positive people![]() • Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock
• Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock![]() • poliomyelitis survivors
• poliomyelitis survivors![]() • Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White
• Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White![]()
Selected virus
Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) is a plant pararetrovirus in the Caulimoviridae family, which has similarities with hepadnaviruses such as hepatitis B virus. It predominantly infects members of the Brassicaceae (cabbage) family, including cauliflower and turnip; some strains can also infect Datura and Nicotiana species of the Solanaceae family. It is transmitted by aphid vectors, such as Myzus persicae. Symptoms include a mottled leaf pattern called "mosaic", necrotic lesions on the surface of infected leaves, stunted growth and deformation of the overall plant structure.
Although the viral genome is double-stranded DNA, the virus replicates via reverse transcription like a retrovirus. The icosahedral virion is 52 nm in diameter, and is built from 420 capsid protein subunits. The circular 8 kb genome encodes seven proteins, including a movement protein, which facilitates viral movement to neighbouring cells, and an insect transmission factor, which recognises a protein receptor at the tip of the aphid mouthparts (pictured). CaMV has several ways of evading the host defensive responses, which include interrupting salicylic acid-dependent signalling and decoying host silencing machinery. The virus has a strong constitutive (always on) promoter, CaMV 35S, which is widely used in plant genetic engineering.
Did you know?
- ...that Hungarian veterinarian József Marek, the first to identify Marek's disease (symptom pictured; right), also developed a remedy for liver fluke in cattle and a nasogastric tube for treating horse colic?
- ...that because photomicrographs of Longan witches broom-associated virus were not published, the virus was not initially accepted as the cause of the eponymous disease?
- ...that Shetlander Johnnie Notions, a physician with no formal medical background, developed a smallpox inoculation that successfully immunised thousands of people before Jenner's vaccine was available?
- ...that the Kivu Ebola epidemic was declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 17 July 2019?
- ...that Larry Kramer frequently invoked the AIDS–Holocaust metaphor and compared Reagan Administration officials to Nazi war criminals?
Selected biography
Many well-known people have survived the paralytic disease polio. The earliest identified case might be Siptah (pictured), Egyptian pharaoh 1197–1191 BC, whose mummified remains have a deformed leg possibly from polio. Claudius, Roman emperor 41–54 AD, walked with a limp after a childhood disease that historians have hypothesised might have been polio. Novelist Sir Walter Scott suffered paralysis in one leg after a teething fever in 1773, which left him lame; his detailed account of his disease has allowed a retrospective diagnosis of polio to be made with confidence.
For many of those who survived it, paralytic polio was a life-changing experience. The disease can lead to permanent physical disability; Itzhak Perlman, for example, plays the violin seated. Others recover completely, with some going on to excel in sports; Ray Ewry became world's foremost standing jumper after childhood polio. Some survivors, including singer Ian Dury and actress Mia Farrow, have campaigned for polio eradication or for disability rights.
In this month
5 June 1981: First report of HIV/AIDS (symbol pictured) appeared in medical literature
6 June 1997: Gene silencing in plants shown to be a viral defence mechanism
7–13 June 1962: Donald Caspar and Aaron Klug proposed the quasi-equivalence principle of virus structure
7–13 June 1962: André Lwoff proposed a viral classification scheme based on nature of genome, type of symmetry and presence of envelope
7–13 June 1962: George Hirst proposed that the influenza virus genome is segmented
9 June 1981: The American Society for Virology was founded
13 June 2012: First case of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) occurred in Saudi Arabia
18 June 1981: A vaccine against foot-and-mouth disease was the first genetically engineered vaccine
21 June 1996: Nevirapine approved, first NNRTI for HIV/AIDS
26 June 1993: Clinical trial of hepatitis B virus drug fialuridine terminated; the drug caused several fatalities due to lactic acidosis
28 June 2011: FAO declared rinderpest eradicated
30 June 1985: Ryan White was denied re-admittance to his school after an AIDS diagnosis, in a case that changed public perceptions of the disease
Selected intervention
Several human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines, including Cervarix and Gardasil, have been approved to protect against infections with particular types of HPV, associated with cervical and other cancers. All vaccines protect against the high-risk HPV types 16 and 18. Gardasil is a quadrivalent vaccine that additionally protects against low-risk HPV-6 and -11, which are associated with most cases of genital warts. A second-generation nine-valent Gardasil vaccine protects against five additional high-risk HPV types. It is estimated that the vaccines may prevent 70% of cervical cancer, 80% of anal cancer, 60% of vaginal cancer, 40% of vulvar cancer and possibly some oropharyngeal cancers. Protection lasts for at least 8–9 years. Some advocate giving Gardasil to men and boys with the primary aim of protecting their female sexual partners; others consider vaccinating only women and girls to be more cost effective. The licensed vaccines are subunit vaccines, containing only the L1 capsid protein of the virus, which self-assembles into virus-like particles. They are not effective in people already infected with HPV. Research is ongoing into therapeutic HPV vaccines including the viral oncoproteins, E6 and E7, but none has yet been licensed.
Subcategories
Subcategories of virology:
Topics
Things to do
- Comment on what you like and dislike about this portal
- Join the Viruses WikiProject
- Tag articles on viruses and virology with the project banner by adding {{WikiProject Viruses}} to the talk page
- Assess unassessed articles against the project standards
- Create requested pages: red-linked viruses | red-linked virus genera
- Expand a virus stub into a full article, adding images, citations, references and taxoboxes, following the project guidelines
- Create a new article (or expand an old one 5-fold) and nominate it for the main page Did You Know? section
- Improve a B-class article and nominate it for Good Article
 or Featured Article
or Featured Article status
status - Suggest articles, pictures, interesting facts, events and news to be featured here on the portal
WikiProjects & Portals
 WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
Medicine • Microbiology • Molecular & Cellular Biology • Veterinary Medicine
Related PortalsAssociated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus


















