Wakayama (city): Difference between revisions
removing hatnote, Wakayama is ambiguous |
|||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 32 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Core city in Honshu, Japan}} |
|||
{{refimprove|date=May 2015}} |
|||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
<!-- See Template:Infobox settlement for additional fields and descriptions --> |
<!-- See Template:Infobox settlement for additional fields and descriptions --> |
||
| name = |
| name = Wakayama |
||
| native_name = |
| native_name = {{nobold|{{lang|ja|和歌山市}}}} |
||
| native_name_lang = ja |
|||
| official_name = Wakayama City |
| official_name = Wakayama City |
||
| settlement_type = [[Core cities of Japan|Core |
| settlement_type = [[Core cities of Japan|Core city]] |
||
| image_skyline = File:Wakayama montage.jpg |
| image_skyline = File:Wakayama montage.jpg |
||
| image_caption = [[Wakayama Castle]], Nishinomaru Garden, [[Saikazaki]], Kimiidera Temple, Downtown Wakayama viewed from the castle keep |
| image_caption = [[Wakayama Castle]], Nishinomaru Garden, [[Saikazaki]], Kimiidera Temple, Downtown Wakayama viewed from the castle keep |
||
| image_flag = Flag of Wakayama, Wakayama. |
| image_flag = Flag of Wakayama, Wakayama.svg |
||
| flag_alt = |
| flag_alt = |
||
| image_seal = |
| image_seal = Emblem of Wakayama, Wakayama.svg |
||
| seal_alt = |
| seal_alt = |
||
| image_shield = |
| image_shield = |
||
| Line 18: | Line 17: | ||
| nickname = |
| nickname = |
||
| motto = |
| motto = |
||
| image_map = {{maplink|frame=yes|frame-align=center|plain=yes|frame-width=265|type=shape|stroke-width=2|stroke-color=#000000|zoom=8}} |
|||
| image_map = Wakayama in Wakayama Prefecture Ja.svg |
|||
| image_map1 = Wakayama in Wakayama Prefecture Ja.svg |
|||
| map_alt = |
| map_alt = |
||
| map_caption = Location of Wakayama in |
| map_caption = Location of Wakayama in Wakayama Prefecture |
||
| image_dot_map = |
| image_dot_map = |
||
| dot_mapsize = |
| dot_mapsize = |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| pushpin_map_alt = |
| pushpin_map_alt = |
||
| pushpin_map_caption = |
| pushpin_map_caption = |
||
| coordinates = {{coord|34|14|N|135|10|E|region:JP-30|display= |
| coordinates = {{coord|34|14|N|135|10|E|region:JP-30|display=it}} |
||
| coor_pinpoint = |
| coor_pinpoint = |
||
| coordinates_footnotes = |
| coordinates_footnotes = |
||
| subdivision_type |
| subdivision_type = Country |
||
| subdivision_name = [[Japan]] |
| subdivision_name = [[Japan]] |
||
| subdivision_type1 = [[List of regions of Japan|Region]] |
| subdivision_type1 = [[List of regions of Japan|Region]] |
||
| subdivision_name1 = [[Honshu]] ([[Kansai region|Kansai]]) |
| subdivision_name1 = [[Honshu]] ([[Kansai region|Kansai]]) |
||
| subdivision_type2 = [[Prefectures of Japan|Prefecture]] |
| subdivision_type2 = [[Prefectures of Japan|Prefecture]] |
||
| subdivision_name2 = [[Wakayama Prefecture]] |
| subdivision_name2 = [[Wakayama Prefecture|Wakayama]] |
||
| subdivision_type3 = |
| subdivision_type3 = |
||
| subdivision_name3 = |
| subdivision_name3 = |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
| area_magnitude = |
| area_magnitude = |
||
| area_footnotes = |
| area_footnotes = |
||
| area_total_km2 = |
| area_total_km2 = 208.84 |
||
| area_total_sq_mi = |
| area_total_sq_mi = |
||
| area_land_km2 = |
| area_land_km2 = |
||
| area_land_sq_mi = |
| area_land_sq_mi = |
||
| area_water_km2 = |
| area_water_km2 = |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
| elevation_ft = |
| elevation_ft = |
||
| population_footnotes = |
| population_footnotes = |
||
| population_total |
| population_total = 351391 |
||
| population_as_of |
| population_as_of = December 1, 2021 |
||
| population_density_km2 |
| population_density_km2 = auto |
||
| population_urban = |
| population_urban = |
||
| population_density_urban_km2 = |
| population_density_urban_km2 = |
||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
| timezone1 = [[Japan Standard Time]] |
| timezone1 = [[Japan Standard Time]] |
||
| utc_offset1 = +9 |
| utc_offset1 = +9 |
||
| timezone1_DST = |
|||
| utc_offset1_DST = |
|||
| postal_code_type = |
| postal_code_type = |
||
| postal_code = |
| postal_code = |
||
| area_code_type = |
| area_code_type = |
||
| area_code = |
| area_code = |
||
| Line 98: | Line 96: | ||
| blank_info_sec2 = |
| blank_info_sec2 = |
||
| blank1_name_sec2 = Address |
| blank1_name_sec2 = Address |
||
| blank1_info_sec2 = |
| blank1_info_sec2 = 23 Shichibancho, Wakayama-shi, Wakayama-ken 640-8511 |
||
| website = {{ |
| website = {{Official|1=http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp/}} |
||
| footnotes = |
| footnotes = |
||
}}{{Infobox Chinese |
|||
}} |
|||
| title = Wakayama |
|||
{{nihongo|'''Wakayama'''|和歌山市|Wakayama-shi|extra={{IPA-ja|ɰakaꜜjama|lang}}}} is the capital [[Cities of Japan|city]] of [[Wakayama Prefecture]] in the [[Kansai region]] of [[Japan]]. |
|||
| pic = Wakayama in Japanese Kanji by Yoko Minchoutai style 横明朝体で日本語の漢字の和歌山.png |
|||
| piccap = ''Wakayama'' in ''[[kanji]]'' |
|||
==Background== |
|||
| picupright = 0.425 |
|||
The city [[population]] rose from 382,155 in 2003 to 386,501 in 2004, a growth of 1.87%. The [[population density]] as of October 1, 2010, was 1,755.47 persons per km². The total area is 209.20 km². |
|||
| kanji = 和歌山 |
|||
| katakana = ワカヤマ |
|||
This population increase has occurred despite Wakayama's beleaguered economy, which has suffered since [[Sumitomo]] Steel moved much of its steel producing operations to [[China]]. The Wakayama steel mills have since been reduced and restructured, with part of the industry completely shutting in 2004. |
|||
| hiragana = わかやま |
|||
| l = Pilgrimage mountain |
|||
| romaji = Wakayama |
|||
| revhep = |
|||
}}[[file:Wakayama city hall03nt3200.jpg|right|thumb|Wakayama City Hall]] |
|||
{{nihongo|'''Wakayama'''|和歌山市|Wakayama-shi|extra={{IPA-ja|wakaꜜjama|pron}}}} is the capital [[Cities of Japan|city]] of [[Wakayama Prefecture]] in the [[Kansai region]] of [[Japan]]. {{As of|2021|12|01}}, the city had an estimated [[population]] of 351,391 in 157066 households and a [[population density]] of 1700 persons per km².<ref name="Wakayama-hp">{{cite web |url=http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp/shisei/wakayama/1001006/1001007/1000509/1041580.html|title= Wakayama city official statistics|location= Japan|language= ja}}</ref> The total area of the city is {{convert|208.84|sqkm|sqmi}}. |
|||
==Geography== |
|||
Wakayama is cleft in two by the [[Kinokawa River]]. The city is bordered at the north by mountains and [[Osaka Prefecture]]. |
|||
Wakayama is located at the northwest corner of Wakayama Prefecture, bordered by Osaka Prefecture to the north and the [[Kii Channel]] and [[Kitan Strait]] to the west. It is located on the mouth of the [[Kinokawa River]] with the main urban center of the city on the river's left bank. |
|||
===Neighboring municipalities=== |
|||
In the city center is [[Wakayama Castle]], built on Mt. Torafusu (the name means "a tiger leaning on his side") in a city central park. During the [[Edo period]], the Kishū [[Tokugawa clan|Tokugawa]] ''[[daimyō]]'' ruled from Wakayama Castle. [[Tokugawa Yoshimune]], the fifth Kishū Tokugawa daimyo, became the eighth [[Tokugawa shogun]]. This castle is a concrete replica of the original, which was destroyed in World War II. |
|||
Wakayama Prefecture |
|||
*[[Kainan, Wakayama|Kainan]] |
|||
Wakayama is home to one of Japan's three [[Musical road#Melody Road|Melody Road]]s, which is made from grooves cut into the pavement, which when driven over causes a tactile vibration and audible rumbling transmitted through the wheels into the car body.<ref name="GuardianJP">{{cite news |first=Bobbie |last=Johnson |title=Japan's melody roads play music as you drive |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2007/nov/13/japan.gadgets |work=[[The Guardian]] |publisher=[[Guardian Media Group|GMG]] |location=[[Farringdon Road]], [[London]], England |page=19 (International section) |date=13 November 2007 |accessdate=20 October 2008 }}</ref><ref name="Noise">{{cite web |url=http://www.noiseaddicts.com/2008/09/car-musical-instrument-melody-roads-japan/ |title=Your car as a musical instrument - Melody Roads |accessdate=20 October 2008 |date=29 September 2008 |publisher=Noise Addicts }}</ref> |
|||
*[[Kinokawa, Wakayama|Kinokawa]] |
|||
*[[Iwade, Wakayama|Iwade]] |
|||
Wakayama Prefecture is famous across Japan for its [[umeboshi]] (salty pickled plums) and [[mikan]] (mandarins). |
|||
Osaka Prefecture |
|||
*[[Hannan, Osaka|Hannan]] |
|||
*[[Misaki, Osaka|Misaki]] |
|||
Hyōgo Prefecture |
|||
*[[Sumoto, Hyōgo]] (separated by the [[Kitan Strait]]) |
|||
==Climate== |
==Climate== |
||
Wakayama has a [[Humid subtropical climate]] (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Wakayama is 15.6 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1713 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 26.4 °C, and lowest in January, at around 5.4 °C.<ref>[https://en.climate-data.org/asia/japan/wakayama-prefecture/wakayama-6178/ Wakayama climate data]</ref> The area is subject to [[typhoon]]s in summer. |
|||
Wakayama has a [[humid subtropical climate]] ([[Köppen climate classification]] ''Cfa'') with hot summers and cool winters. Precipitation is significant throughout the year, and is greater in summer than in winter. |
|||
{{Weather box|width=auto |
{{Weather box |
||
|width=auto |
|||
|collapsed = Y |
|||
|location = Wakayama, Wakayama |
|||
|single line = Y |
|single line = Y |
||
|metric first = Y |
|metric first = Y |
||
|location = Wakayama (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1879−present) |
|||
|Jan high C = 9.5 |
|||
| |
|Jan record high C = 21.2 |
||
| |
|Feb record high C = 22.0 |
||
| |
|Mar record high C = 24.5 |
||
| |
|Apr record high C = 30.0 |
||
| |
|May record high C = 32.4 |
||
| |
|Jun record high C = 35.3 |
||
| |
|Jul record high C = 37.8 |
||
| |
|Aug record high C = 38.5 |
||
| |
|Sep record high C = 35.8 |
||
| |
|Oct record high C = 32.3 |
||
| |
|Nov record high C = 27.7 |
||
| |
|Dec record high C = 25.2 |
||
| |
|Jan record low C = -6.0 |
||
| |
|Feb record low C = -5.4 |
||
| |
|Mar record low C = -4.0 |
||
| |
|Apr record low C = -1.4 |
||
| |
|May record low C = 3.7 |
||
| |
|Jun record low C = 9.0 |
||
| |
|Jul record low C = 14.4 |
||
| |
|Aug record low C = 13.5 |
||
| |
|Sep record low C = 11.2 |
||
| |
|Oct record low C = 4.3 |
||
| |
|Nov record low C = -0.6 |
||
| |
|Dec record low C = -3.0 |
||
|Feb low C = 2.0 |
|||
|Mar low C = 4.4 |
|||
|Apr low C = 10.0 |
|||
|May low C = 14.4 |
|||
|Jun low C = 19.1 |
|||
|Jul low C = 23.4 |
|||
|Aug low C = 24.0 |
|||
|Sep low C = 20.3 |
|||
|Oct low C = 13.9 |
|||
|Nov low C = 8.6 |
|||
|Dec low C = 4.1 |
|||
|precipitation colour = green |
|precipitation colour = green |
||
|Jan precipitation mm = |
|Jan precipitation mm = 48.7 |
||
|Feb precipitation mm = |
|Feb precipitation mm = 62.0 |
||
|Mar precipitation mm = |
|Mar precipitation mm = 96.9 |
||
|Apr precipitation mm = |
|Apr precipitation mm = 98.4 |
||
|May precipitation mm = |
|May precipitation mm = 146.6 |
||
|Jun precipitation mm = |
|Jun precipitation mm = 183.5 |
||
|Jul precipitation mm = |
|Jul precipitation mm = 175.8 |
||
|Aug precipitation mm = |
|Aug precipitation mm = 101.8 |
||
|Sep precipitation mm = |
|Sep precipitation mm = 181.3 |
||
|Oct precipitation mm = |
|Oct precipitation mm = 160.8 |
||
|Nov precipitation mm = |
|Nov precipitation mm = 95.9 |
||
|Dec precipitation mm = |
|Dec precipitation mm = 62.7 |
||
|year precipitation mm = 1414.4 |
|||
|Jan snow cm = 1 |
|||
|Jan mean C = 6.2 |
|||
|Feb mean C = 6.7 |
|||
|Mar mean C = 9.9 |
|||
|Apr mean C = 15.1 |
|||
|May mean C = 19.7 |
|||
|Jun mean C = 23.2 |
|||
|Jul mean C = 27.2 |
|||
|Aug mean C = 28.4 |
|||
|Sep mean C = 24.9 |
|||
|Oct mean C = 19.3 |
|||
|Nov mean C = 13.8 |
|||
|Dec mean C = 8.6 |
|||
|year mean C = 16.9 |
|||
|Jan high C = 9.8 |
|||
|Feb high C = 10.7 |
|||
|Mar high C = 14.3 |
|||
|Apr high C = 19.7 |
|||
|May high C = 24.3 |
|||
|Jun high C = 27.1 |
|||
|Jul high C = 31.1 |
|||
|Aug high C = 32.6 |
|||
|Sep high C = 29.0 |
|||
|Oct high C = 23.4 |
|||
|Nov high C = 17.9 |
|||
|Dec high C = 12.5 |
|||
|year high C = 21.0 |
|||
|Jan low C = 2.9 |
|||
|Feb low C = 3.1 |
|||
|Mar low C = 5.8 |
|||
|Apr low C = 10.7 |
|||
|May low C = 15.6 |
|||
|Jun low C = 20.1 |
|||
|Jul low C = 24.3 |
|||
|Aug low C = 25.1 |
|||
|Sep low C = 21.5 |
|||
|Oct low C = 15.6 |
|||
|Nov low C = 9.9 |
|||
|Dec low C = 5.1 |
|||
|year low C = 13.3 |
|||
|Jan humidity = 61 |
|||
|Feb humidity = 61 |
|||
|Mar humidity = 60 |
|||
|Apr humidity = 61 |
|||
|May humidity = 64 |
|||
|Jun humidity = 72 |
|||
|Jul humidity = 73 |
|||
|Aug humidity = 70 |
|||
|Sep humidity = 69 |
|||
|Oct humidity = 67 |
|||
|Nov humidity = 66 |
|||
|Dec humidity = 63 |
|||
|year humidity = 66 |
|||
|Jan sun = 135.8 |
|||
|Feb sun = 143.1 |
|||
|Mar sun = 179.6 |
|||
|Apr sun = 196.9 |
|||
|May sun = 207.6 |
|||
|Jun sun = 157.6 |
|||
|Jul sun = 206.1 |
|||
|Aug sun = 239.9 |
|||
|Sep sun = 173.2 |
|||
|Oct sun = 169.9 |
|||
|Nov sun = 147.7 |
|||
|Dec sun = 135.4 |
|||
|year sun = 2100.1 |
|||
|Jan snow cm = 0 |
|||
|Feb snow cm = 1 |
|Feb snow cm = 1 |
||
|Mar snow cm = |
|Mar snow cm = 0 |
||
|Apr snow cm = 0 |
|Apr snow cm = 0 |
||
|May snow cm = 0 |
|May snow cm = 0 |
||
| Line 185: | Line 251: | ||
|Nov snow cm = 0 |
|Nov snow cm = 0 |
||
|Dec snow cm = 0 |
|Dec snow cm = 0 |
||
| |
|year snow cm = 1 |
||
|unit precipitation days = 0.5 mm |
|||
|Feb humidity = 63 |
|||
|Jan precipitation days = 7.2 |
|||
|Mar humidity = 62 |
|||
|Feb precipitation days = 7.9 |
|||
|Apr humidity = 65 |
|||
|Mar precipitation days = 10.3 |
|||
|May humidity = 68 |
|||
|Apr precipitation days = 10.0 |
|||
|Jun humidity = 75 |
|||
|May precipitation days = 10.4 |
|||
|Jul humidity = 76 |
|||
|Jun precipitation days = 12.5 |
|||
|Aug humidity = 73 |
|||
|Jul precipitation days = 10.6 |
|||
|Sep humidity = 73 |
|||
|Aug precipitation days = 7.2 |
|||
|Oct humidity = 70 |
|||
|Sep precipitation days = 10.2 |
|||
|Nov humidity = 68 |
|||
|Oct precipitation days = 9.6 |
|||
|Dec humidity = 66 |
|||
|Nov precipitation days = 7.3 |
|||
|Jan sun = 137.1 |
|||
|Dec precipitation days = 7.7 |
|||
|Feb sun = 134.2 |
|||
|year precipitation days = 111.1 |
|||
|Mar sun = 175.6 |
|||
|source 1 = Japan Meteorological Agency<ref>{{cite web |
|||
|Apr sun = 180.3 |
|||
| url = https://www.data.jma.go.jp/obd/stats/etrn/index.php?prec_no=65&block_no=47777&year=&month=&day=&view= |
|||
|May sun = 203.7 |
|||
|script-title=ja:気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値) |
|||
|Jun sun = 161.2 |
|||
| publisher = [[Japan Meteorological Agency]] |
|||
|Jul sun = 207.2 |
|||
| access-date = May 19, 2021}}</ref> |
|||
|Aug sun = 228.3 |
|||
}} |
|||
|Sep sun = 162.1 |
|||
|Oct sun = 164.2 |
|||
==Demographics== |
|||
|Nov sun = 142.2 |
|||
Per Japanese census data,<ref>[https://www.citypopulation.de/php/japan-wakayama.php Wakayama population statistics]</ref> the population of Wakayama peaked in the 1980s and has been declining slowly since. |
|||
|Dec sun = 134.9 |
|||
|source 1 = NOAA (1961-1990)<ref name= NOAA>{{cite web |
|||
{{Historical populations |
|||
|url = ftp://ftp.atdd.noaa.gov/pub/GCOS/WMO-Normals/RA-II/JP/47777.TXT |
|||
| 1960 | 285155 |
|||
|title = Wakayama Climate Normals 1961-1990 |
|||
| 1970 | 365267 |
|||
|publisher = [[National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration]] |
|||
| 1980 | 400802 |
|||
|accessdate = January 6, 2013}}</ref> |
|||
| 1990 | 396553 |
|||
|date=January 2013}} |
|||
| 2000 | 386551 |
|||
| 2010 | 369400 |
|||
|align = none |
|||
| footnote = |
|||
}} |
|||
==History== |
|||
The area of the modern city of Wakayama was the center of ancient [[Kii Province]], and the [[Iwase-Senzuka Kofun Cluster]] is one of the largest clusters of ''[[kofun]]'' [[burial mound]]s in Japan. The area the home of the ''Kii [[Kuni no miyatsuko]]'', a local king ruling the Kinokawa River Valley prior to the rise of the [[Yamato State]]. During the [[Nara period]] priests from [[Tang Dynasty|Tang China]] built the [[Kimii-dera temple]]. From the [[Muromachi period]], Waka-no-ura was a port on the Kinokawa River, and [[Toyotomi Hideyoshi]] constructed the predecessor of [[Wakayama Castle]] during his conquest of Kii Province during the [[Sengoku period]]. During the [[Edo period]], the [[jōkamachi|castle town]] at the base of Wakayama Castle grew and prospered under the rule of the [[Kishū Tokugawa family|Kii Tokugawa clan]] as the center of [[Kishū Domain]]. After the [[Meiji restoration]], Wakayama was granted city status on April 1, 1889 with the creation of the modern municipalities system. The city suffered 1208 deaths and 1560 critically wounded in the July 9, 1945 [[Bombing of Wakayama during World War II]], which destroyed more than half of the urban area. On April 1, 1997, Wakayama attained [[Core cities of Japan|core city]] status, with increased local autonomy. |
|||
==Government== |
|||
Wakayama has a [[mayor-council]] form of government with a directly elected mayor and a [[unicameral]] city council of 38 members. Wakayama contributes 15 members to the Wakayama Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is divided between Wakayama 1st district and Wakayama 2nd district of the [[House of Representatives of Japan|lower house]] of the [[Diet of Japan]]. |
|||
==Economy== |
|||
Wakayama is the main commercial city of northern Wakayama and is the largest city in Wakayama Prefecture. Primary industries include agriculture, notably rice and citrus fruits, and [[commercial fishing]]. Secondary industries are centered around electronics and heavy industry. [[Nippon Steel]] remains a major employer, although the city suffered considerably when former Sumitomo Steel shifted much of its production to China. Other major employers include [[Kao Corporation]] and [[Mitsubishi Electric]]. |
|||
==Education== |
|||
===Colleges and Universities=== |
|||
*[[Wakayama University]] |
|||
*[[Wakayama Medical University]] |
|||
*[[Wakayama Shin-ai University]] |
|||
*[[Wakayama College of Science Studies]] |
|||
*[[Tokyo Health Care University]] School of Nursing |
|||
*[[Takarazuka University of Medical and Health Care]] MedicalSchool |
|||
===Primary and secondary education=== |
|||
Wakayama has 50 public elementary schools, 19 public middle schools and one public high school operated by the city government and one private elementary school and three private middle schools. The Wakayama Prefectural Board of Education operates two public middle schools and 10 public high schools. There are also four private high schools.In addition, there is one elementary school and one high school run by Wakayama University. |
|||
The prefecture also operates five special education school for the handicapped, and one more is operated by Wakayama University. |
|||
The city has one [[Chosun gakko|North Korean school]], {{Nihongo|{{ill|Wakayama Korean Elementary and Middle School|ja|和歌山朝鮮初中級学校}}|和歌山朝鮮初中級学校}}.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.chongryon.com/j/cr/link3.html |script-title=ja:ウリハッキョ一覧 |publisher=[[Chongryon]] |access-date=October 14, 2015}} ([https://web.archive.org/web/20151219132215/http://www.chongryon.com/j/cr/link3.html Archive]).</ref> |
|||
==Transportation== |
==Transportation== |
||
===Railway=== |
|||
*'''[[West Japan Railway Company]]''' |
|||
[[File:JR logo (west).svg|20px]] [[West Japan Railway Company|JR West]] – [[Hanwa Line]] |
|||
**[[Kisei Main Line]] |
|||
* {{STN|Kii}} - {{STN|Musota}} - {{STN|Kii-Nakanoshima}} - {{STN|Wakayama}} |
|||
**[[Hanwa Line]] |
|||
[[File:JR logo (west).svg|20px]] [[West Japan Railway Company|JR West]] – [[Kisei Main Line]] |
|||
**[[Wakayama Line]] |
|||
* {{STN|Kimiidera}} - {{STN|Miyamae}} - {{STN|Wakayama}} - {{STN|Kiwa|Wakayama}} - {{STN|Wakayamashi}} |
|||
*'''[[Wakayama Electric Railway]]''' |
|||
[[File:JR logo (west).svg|20px]] [[West Japan Railway Company|JR West]] – [[Wakayama Line]] |
|||
**[[Kishigawa Line]] |
|||
*{{STN|Kii-Ogura}} - {{STN|Hoshiya}} - {{STN|Senda}} - {{STN|Tainose}} - {{STN|Wakayama}} |
|||
[[File:Ryobi Group logo.svg|20px]] Wakayama Electric Railway [[Kishigawa Line]] |
|||
* {{STN|Wakayama}} - {{STN|Tanakaguchi}} - {{STN|Nichizengū}} - {{STN|Kōzaki|Wakayama}} - {{STN|Kamayama}} - {{STN|Kōtsū Center Mae}} - {{STN|Okazakimae}} - {{STN|Kire}} - {{STN|Idakiso}} - {{STN|Sandō}} |
|||
[[File:Nankai group logo.svg|15px]] [[Nankai Electric Railway]] [[Nankai Main Line]] |
|||
* {{STN|Wakayamadaigakumae}} - {{STN|Kinokawa}} - {{STN|Wakayamashi}} |
|||
[[File:Nankai group logo.svg|15px]] [[Nankai Electric Railway]] [[Wakayamako Line]] |
|||
* {{STN|Wakayamashi}} - {{STN|Wakayamakō}} |
|||
[[File:Nankai group logo.svg|15px]] [[Nankai Electric Railway]] [[Kada Line]] |
|||
* {{STN|Wakayamashi}} - {{STN|Kinokawa}} - {{STN|Higashi-Matsue|Wakayama|Higashi-Matsue}} - {{STN|Nakamatsue}} - {{STN|Hachimanmae|Wakayama}} - {{STN|Nishinoshō}} - {{STN|Nirigahama}} - {{STN|Isonoura}} - {{STN|Kada}} |
|||
===Bus=== |
|||
==Sightseeing spots== |
|||
* [https://www.wakayamabus.co.jp/english/ Wakayama Bus] |
|||
===Highway=== |
|||
* [[File:JP Expressway E42.svg|30px|link=|alt=]] [[Hanwa Expressway]] |
|||
* [[File:JP Expressway E24.svg|30px|link=|alt=]] [[Keinawa Expressway]] |
|||
* {{jct|country=JPN|Route|24}} |
|||
* {{jct|country=JPN|Route|26}} |
|||
* {{jct|country=JPN|Route|42}} |
|||
==Sister cities== |
|||
Wakayama has [[Town twinning|sister-city]] relationships with four overseas municipalities:<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp/english/sister.html |title=Wakayama City: English Language Resources Center |access-date=2011-02-19 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110220043007/http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp/english/sister.html |archive-date=2011-02-20 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
*{{flagdeco|United States}} [[Bakersfield, California|Bakersfield]], [[California]], United States |
|||
*{{flagdeco|South Korea}} [[Jeju City|Jeju]], [[Jeju Province]], South Korea |
|||
*{{flagdeco|Canada}} [[Richmond, British Columbia|Richmond]], [[British Columbia]], Canada |
|||
*{{flagdeco|PRC}} [[Jinan]], [[Shandong]], China |
|||
Wakayama City formed a sister-city relationship with the city of [[Jinan]] mainly due to the efforts of {{Nihongo|Hiroshi Yamazaki|山崎 宏}}, who was an escaped medic in the [[Imperial Japanese Army]] and stayed in China after the war. He married and runs his own clinic in China. In 1976, he visited Wakayama after nearly 40 years.{{Citation needed|date=May 2010}} |
|||
==Local attractions== |
|||
*[[Wakayama Castle]] |
*[[Wakayama Castle]] |
||
*[[ |
*[[Kimiidera]] |
||
*Kimiidera |
|||
*[[Hinokuma Shrine]] |
*[[Hinokuma Shrine]] |
||
*[[Itakiso Shrine]] |
|||
*[[Kamayama Shrine]] |
*[[Kamayama Shrine]] |
||
*[[Kishū Tōshō-gū]] |
*[[Kishū Tōshō-gū]] |
||
*Wakayama Marina City<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp/english/destinations.html#marinacity| |
*Wakayama Marina City<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp/english/destinations.html#marinacity|access-date=26 August 2015|title=Wakayama City: English Language Resources Center|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923204145/http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp/english/destinations.html#marinacity|archive-date=23 September 2015|url-status=dead|df=dmy-all}}</ref> |
||
*The Museum of Modern Art, Wakayama |
*The Museum of Modern Art, Wakayama |
||
* Wakayama is home to one of Japan's three [[Musical road#Melody Road|Melody Road]]s, which is made from grooves cut into the pavement, which when driven over causes a tactile vibration and audible rumbling transmitted through the wheels into the car body.<ref name="GuardianJP">{{cite news |first=Bobbie |last=Johnson |title=Japan's melody roads play music as you drive |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2007/nov/13/japan.gadgets |work=[[The Guardian]] |publisher=[[Guardian Media Group|GMG]] |location=[[Farringdon Road]], [[London]], England |page=19 (International section) |date=13 November 2007 |access-date=20 October 2008 }}</ref><ref name="Noise">{{cite web |url=http://www.noiseaddicts.com/2008/09/car-musical-instrument-melody-roads-japan/ |title=Your car as a musical instrument - Melody Roads |access-date=20 October 2008 |date=29 September 2008 |publisher=Noise Addicts }}</ref> |
|||
Wakayama Prefecture is famous across Japan for its [[umeboshi]] (salty pickled plums) and [[mikan]] (mandarins). |
|||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
File:Wakanoura Art Cube Wakayama Japan01n.jpg|Art Cube of Wakanoura |
File:Wakanoura Art Cube Wakayama Japan01n.jpg|Art Cube of Wakanoura |
||
| Line 238: | Line 365: | ||
File:121013 The museum of modern art, wakayama01s3.jpg|The Museum of Modern Art, Wakayama |
File:121013 The museum of modern art, wakayama01s3.jpg|The Museum of Modern Art, Wakayama |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
==Education== |
|||
{{expand section|date=October 2015}} |
|||
The city has a [[Chosun gakko|North Korean school]], Wakayama Korean Elementary and Middle School ([[:ja:和歌山朝鮮初中級学校|和歌山朝鮮初中級学校]]).<ref>"[http://www.chongryon.com/j/cr/link3.html ウリハッキョ一覧]" ([https://www.webcitation.org/6cGktqdmJ?url=http://www.chongryon.com/j/cr/link3.html Archive]). [[Chongryon]]. Retrieved on October 14, 2015.</ref> |
|||
==Sister cities== |
|||
Wakayama has [[Town twinning|sister-city]] relationships with four overseas municipalities:<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp/english/sister.html |title=Archived copy |access-date=2011-02-19 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110220043007/http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp/english/sister.html |archive-date=2011-02-20 |dead-url=yes |df= }}</ref> |
|||
*{{flagicon|United States}} [[Bakersfield, California|Bakersfield]], [[California]], [[United States]] |
|||
*{{flagicon|South Korea}} [[Jeju City|Jeju]], [[South Korea]] |
|||
*{{flagicon|Canada}} [[Richmond, British Columbia|Richmond]], [[British Columbia]], [[Canada]] |
|||
*{{flagicon|PRC}} [[Jinan]], [[Shandong]], [[People's Republic of China|China]] |
|||
Wakayama City formed a sister-city relationship with the city of [[Jinan]] in China mainly due to the efforts of Hiroshi Yamazaki (山崎 宏), who was an escaped medic in the [[Imperial Japanese Army]] and stayed in China after the war. He married and runs his own clinic in China. In 1976, he visited Wakayama after nearly 40 years.{{Citation needed|date=May 2010}} |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 257: | Line 372: | ||
{{Commons category|Wakayama, Wakayama}} |
{{Commons category|Wakayama, Wakayama}} |
||
{{Wikivoyage|Wakayama}} |
{{Wikivoyage|Wakayama}} |
||
* [http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp Wakayama City official website] {{ |
* [http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp Wakayama City official website] {{in lang|ja}} |
||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20050213140225/http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp/english/ Wakayama City official website] {{ |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20050213140225/http://www.city.wakayama.wakayama.jp/english/ Wakayama City official website] {{in lang|en}} |
||
* [https://www.youtube.com/user/wakayamacitychannel Wakayama City official Youtube channel]{{ |
* [https://www.youtube.com/user/wakayamacitychannel Wakayama City official Youtube channel]{{in lang|ja}} |
||
* [http://www.wakayamakanko.com/eng/ Wakayama City Tourist Association] {{ |
* [http://www.wakayamakanko.com/eng/ Wakayama City Tourist Association] {{in lang|en}} |
||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20130818081742/http://www.wakayama-kanko.or.jp/walkingmap/en/ Waiker's Guide Map to Wakayama] {{ |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20130818081742/http://www.wakayama-kanko.or.jp/walkingmap/en/ Waiker's Guide Map to Wakayama] {{in lang|en}} |
||
* {{osmrelation-inline|1919929|Wakayama}} |
* {{osmrelation-inline|1919929|Wakayama}} |
||
| Line 267: | Line 382: | ||
{{Metropolitan cities of Japan}} |
{{Metropolitan cities of Japan}} |
||
{{Most populous cities in Japan}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
[[Category:Wakayama (city)| ]] |
|||
[[Category:Cities in Wakayama Prefecture]] |
[[Category:Cities in Wakayama Prefecture]] |
||
[[Category:Port settlements in Japan]] |
[[Category:Port settlements in Japan]] |
||
[[Category:Populated coastal places in Japan]] |
[[Category:Populated coastal places in Japan]] |
||
[[Category:Wakayama, Wakayama| ]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 05:27, 29 March 2024
Wakayama
和歌山市 | |
|---|---|
| Wakayama City | |
 Wakayama Castle, Nishinomaru Garden, Saikazaki, Kimiidera Temple, Downtown Wakayama viewed from the castle keep | |
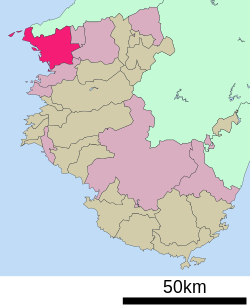
 Location of Wakayama in Wakayama Prefecture | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 34°14′N 135°10′E / 34.233°N 135.167°E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Honshu (Kansai) |
| Prefecture | Wakayama |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Masahiro Obana |
| Area | |
| • Total | 208.84 km2 (80.63 sq mi) |
| Population (December 1, 2021) | |
| • Total | 351,391 |
| • Density | 1,700/km2 (4,400/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| - Tree | Cinnamomum camphora |
| - Flower | Azalea |
| Address | 23 Shichibancho, Wakayama-shi, Wakayama-ken 640-8511 |
| Website | Official website |
| Wakayama | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Wakayama in kanji | |||||
| Japanese name | |||||
| Kanji | 和歌山 | ||||
| Hiragana | わかやま | ||||
| Katakana | ワカヤマ | ||||
| |||||

Wakayama (和歌山市, Wakayama-shi, pronounced [wakaꜜjama]) is the capital city of Wakayama Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan. As of 1 December 2021[update], the city had an estimated population of 351,391 in 157066 households and a population density of 1700 persons per km².[1] The total area of the city is 208.84 square kilometres (80.63 sq mi).
Geography[edit]
Wakayama is located at the northwest corner of Wakayama Prefecture, bordered by Osaka Prefecture to the north and the Kii Channel and Kitan Strait to the west. It is located on the mouth of the Kinokawa River with the main urban center of the city on the river's left bank.
Neighboring municipalities[edit]
Wakayama Prefecture
Osaka Prefecture
Hyōgo Prefecture
- Sumoto, Hyōgo (separated by the Kitan Strait)
Climate[edit]
Wakayama has a Humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa) characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Wakayama is 15.6 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1713 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 26.4 °C, and lowest in January, at around 5.4 °C.[2] The area is subject to typhoons in summer.
| Climate data for Wakayama (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1879−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 21.2 (70.2) |
22.0 (71.6) |
24.5 (76.1) |
30.0 (86.0) |
32.4 (90.3) |
35.3 (95.5) |
37.8 (100.0) |
38.5 (101.3) |
35.8 (96.4) |
32.3 (90.1) |
27.7 (81.9) |
25.2 (77.4) |
38.5 (101.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 9.8 (49.6) |
10.7 (51.3) |
14.3 (57.7) |
19.7 (67.5) |
24.3 (75.7) |
27.1 (80.8) |
31.1 (88.0) |
32.6 (90.7) |
29.0 (84.2) |
23.4 (74.1) |
17.9 (64.2) |
12.5 (54.5) |
21.0 (69.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.2 (43.2) |
6.7 (44.1) |
9.9 (49.8) |
15.1 (59.2) |
19.7 (67.5) |
23.2 (73.8) |
27.2 (81.0) |
28.4 (83.1) |
24.9 (76.8) |
19.3 (66.7) |
13.8 (56.8) |
8.6 (47.5) |
16.9 (62.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 2.9 (37.2) |
3.1 (37.6) |
5.8 (42.4) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.6 (60.1) |
20.1 (68.2) |
24.3 (75.7) |
25.1 (77.2) |
21.5 (70.7) |
15.6 (60.1) |
9.9 (49.8) |
5.1 (41.2) |
13.3 (55.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −6.0 (21.2) |
−5.4 (22.3) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
3.7 (38.7) |
9.0 (48.2) |
14.4 (57.9) |
13.5 (56.3) |
11.2 (52.2) |
4.3 (39.7) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 48.7 (1.92) |
62.0 (2.44) |
96.9 (3.81) |
98.4 (3.87) |
146.6 (5.77) |
183.5 (7.22) |
175.8 (6.92) |
101.8 (4.01) |
181.3 (7.14) |
160.8 (6.33) |
95.9 (3.78) |
62.7 (2.47) |
1,414.4 (55.69) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 0 (0) |
1 (0.4) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
1 (0.4) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 7.2 | 7.9 | 10.3 | 10.0 | 10.4 | 12.5 | 10.6 | 7.2 | 10.2 | 9.6 | 7.3 | 7.7 | 111.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 61 | 61 | 60 | 61 | 64 | 72 | 73 | 70 | 69 | 67 | 66 | 63 | 66 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 135.8 | 143.1 | 179.6 | 196.9 | 207.6 | 157.6 | 206.1 | 239.9 | 173.2 | 169.9 | 147.7 | 135.4 | 2,100.1 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[3] | |||||||||||||
Demographics[edit]
Per Japanese census data,[4] the population of Wakayama peaked in the 1980s and has been declining slowly since.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 285,155 | — |
| 1970 | 365,267 | +28.1% |
| 1980 | 400,802 | +9.7% |
| 1990 | 396,553 | −1.1% |
| 2000 | 386,551 | −2.5% |
| 2010 | 369,400 | −4.4% |
History[edit]
The area of the modern city of Wakayama was the center of ancient Kii Province, and the Iwase-Senzuka Kofun Cluster is one of the largest clusters of kofun burial mounds in Japan. The area the home of the Kii Kuni no miyatsuko, a local king ruling the Kinokawa River Valley prior to the rise of the Yamato State. During the Nara period priests from Tang China built the Kimii-dera temple. From the Muromachi period, Waka-no-ura was a port on the Kinokawa River, and Toyotomi Hideyoshi constructed the predecessor of Wakayama Castle during his conquest of Kii Province during the Sengoku period. During the Edo period, the castle town at the base of Wakayama Castle grew and prospered under the rule of the Kii Tokugawa clan as the center of Kishū Domain. After the Meiji restoration, Wakayama was granted city status on April 1, 1889 with the creation of the modern municipalities system. The city suffered 1208 deaths and 1560 critically wounded in the July 9, 1945 Bombing of Wakayama during World War II, which destroyed more than half of the urban area. On April 1, 1997, Wakayama attained core city status, with increased local autonomy.
Government[edit]
Wakayama has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city council of 38 members. Wakayama contributes 15 members to the Wakayama Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is divided between Wakayama 1st district and Wakayama 2nd district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy[edit]
Wakayama is the main commercial city of northern Wakayama and is the largest city in Wakayama Prefecture. Primary industries include agriculture, notably rice and citrus fruits, and commercial fishing. Secondary industries are centered around electronics and heavy industry. Nippon Steel remains a major employer, although the city suffered considerably when former Sumitomo Steel shifted much of its production to China. Other major employers include Kao Corporation and Mitsubishi Electric.
Education[edit]
Colleges and Universities[edit]
- Wakayama University
- Wakayama Medical University
- Wakayama Shin-ai University
- Wakayama College of Science Studies
- Tokyo Health Care University School of Nursing
- Takarazuka University of Medical and Health Care MedicalSchool
Primary and secondary education[edit]
Wakayama has 50 public elementary schools, 19 public middle schools and one public high school operated by the city government and one private elementary school and three private middle schools. The Wakayama Prefectural Board of Education operates two public middle schools and 10 public high schools. There are also four private high schools.In addition, there is one elementary school and one high school run by Wakayama University.
The prefecture also operates five special education school for the handicapped, and one more is operated by Wakayama University.
The city has one North Korean school, Wakayama Korean Elementary and Middle School (和歌山朝鮮初中級学校).[5]
Transportation[edit]
Railway[edit]
- Kii - Musota - Kii-Nakanoshima - Wakayama
- Kimiidera - Miyamae - Wakayama - Kiwa - Wakayamashi
![]() Wakayama Electric Railway Kishigawa Line
Wakayama Electric Railway Kishigawa Line
- Wakayama - Tanakaguchi - Nichizengū - Kōzaki - Kamayama - Kōtsū Center Mae - Okazakimae - Kire - Idakiso - Sandō
![]() Nankai Electric Railway Nankai Main Line
Nankai Electric Railway Nankai Main Line
![]() Nankai Electric Railway Wakayamako Line
Nankai Electric Railway Wakayamako Line
![]() Nankai Electric Railway Kada Line
Nankai Electric Railway Kada Line
- Wakayamashi - Kinokawa - Higashi-Matsue - Nakamatsue - Hachimanmae - Nishinoshō - Nirigahama - Isonoura - Kada
Bus[edit]
Highway[edit]
Sister cities[edit]
Wakayama has sister-city relationships with four overseas municipalities:[6]
 Bakersfield, California, United States
Bakersfield, California, United States Jeju, Jeju Province, South Korea
Jeju, Jeju Province, South Korea Richmond, British Columbia, Canada
Richmond, British Columbia, Canada Jinan, Shandong, China
Jinan, Shandong, China
Wakayama City formed a sister-city relationship with the city of Jinan mainly due to the efforts of Hiroshi Yamazaki (山崎 宏), who was an escaped medic in the Imperial Japanese Army and stayed in China after the war. He married and runs his own clinic in China. In 1976, he visited Wakayama after nearly 40 years.[citation needed]
Local attractions[edit]
- Wakayama Castle
- Kimiidera
- Hinokuma Shrine
- Itakiso Shrine
- Kamayama Shrine
- Kishū Tōshō-gū
- Wakayama Marina City[7]
- The Museum of Modern Art, Wakayama
- Wakayama is home to one of Japan's three Melody Roads, which is made from grooves cut into the pavement, which when driven over causes a tactile vibration and audible rumbling transmitted through the wheels into the car body.[8][9]
Wakayama Prefecture is famous across Japan for its umeboshi (salty pickled plums) and mikan (mandarins).
-
Art Cube of Wakanoura
-
Kimiidera
-
The Museum of Modern Art, Wakayama
References[edit]
- ^ "Wakayama city official statistics" (in Japanese). Japan.
- ^ Wakayama climate data
- ^ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved May 19, 2021.
- ^ Wakayama population statistics
- ^ ウリハッキョ一覧. Chongryon. Retrieved October 14, 2015. (Archive).
- ^ "Wakayama City: English Language Resources Center". Archived from the original on 2011-02-20. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
- ^ "Wakayama City: English Language Resources Center". Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 26 August 2015.
- ^ Johnson, Bobbie (13 November 2007). "Japan's melody roads play music as you drive". The Guardian. Farringdon Road, London, England: GMG. p. 19 (International section). Retrieved 20 October 2008.
- ^ "Your car as a musical instrument - Melody Roads". Noise Addicts. 29 September 2008. Retrieved 20 October 2008.
External links[edit]
- Wakayama City official website (in Japanese)
- Wakayama City official website (in English)
- Wakayama City official Youtube channel(in Japanese)
- Wakayama City Tourist Association (in English)
- Waiker's Guide Map to Wakayama (in English)
 Geographic data related to Wakayama at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Wakayama at OpenStreetMap







